Laser micromachining
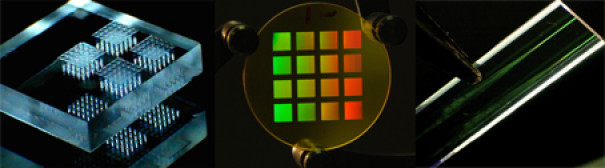
Femtosecond laser machining has particular advantages: The heat deposit is smaller compared to nanosecond and picosecond lasers. Moreover, if the intensity is high enough, it is not limited by the material. For laser intensities above 1012 W/cm2 nearly all materials become metallic and the material is removed via microscopic plasma formation and expansion.

Your direct line to our expert: Dr. Christian Mauser

